IDIOMA
My Role: Designer
Platform: IOS
Current State: Finished
Fall 2012
North Carolina State University, College of Design
User Experience Design
Idioma was a design project at NC State University and the goal was to create a course software for anthropology and social science students. The software offers different tools and features for contextual learning.
Through this project following objective were considered:
- Identify key cognitive behaviors related to critical and creative thinking, using literature to support definitions.
- Examine traditional methods of delivering college instruction in the sciences, social sciences, and humanities, as well as aspects of the co-curriculum that contribute to learning;
- Design prototypes that enhance students’ critical and creative viewing, listening, and reading in one of the disciplines, with special attention to the affordances of technology;
- Practice the steps of building a design investigation (for thesis students- model the process of defining a problem area, identifying research opportunities, prototyping a speculative object, and demonstrating its application).

The task was to design something that supports a particular course (or activity in the case of the co-curriculum) that engages students in critical and creative thinking through critical and creative methods that are characteristic of design. The solution needs to be generalizable to other courses within the general domain. Through the design research phase following methods were used:
- User Interview and Surveys
- Literature Review
- Persona
- User Journey Map
- Task Flow
- Concept Mapping
- Prototyping
The software has 10 consecutive steps (features) for the course that all student need to take in order to get the final score. Following are three prototypes for three steps out of then.

Research Poster
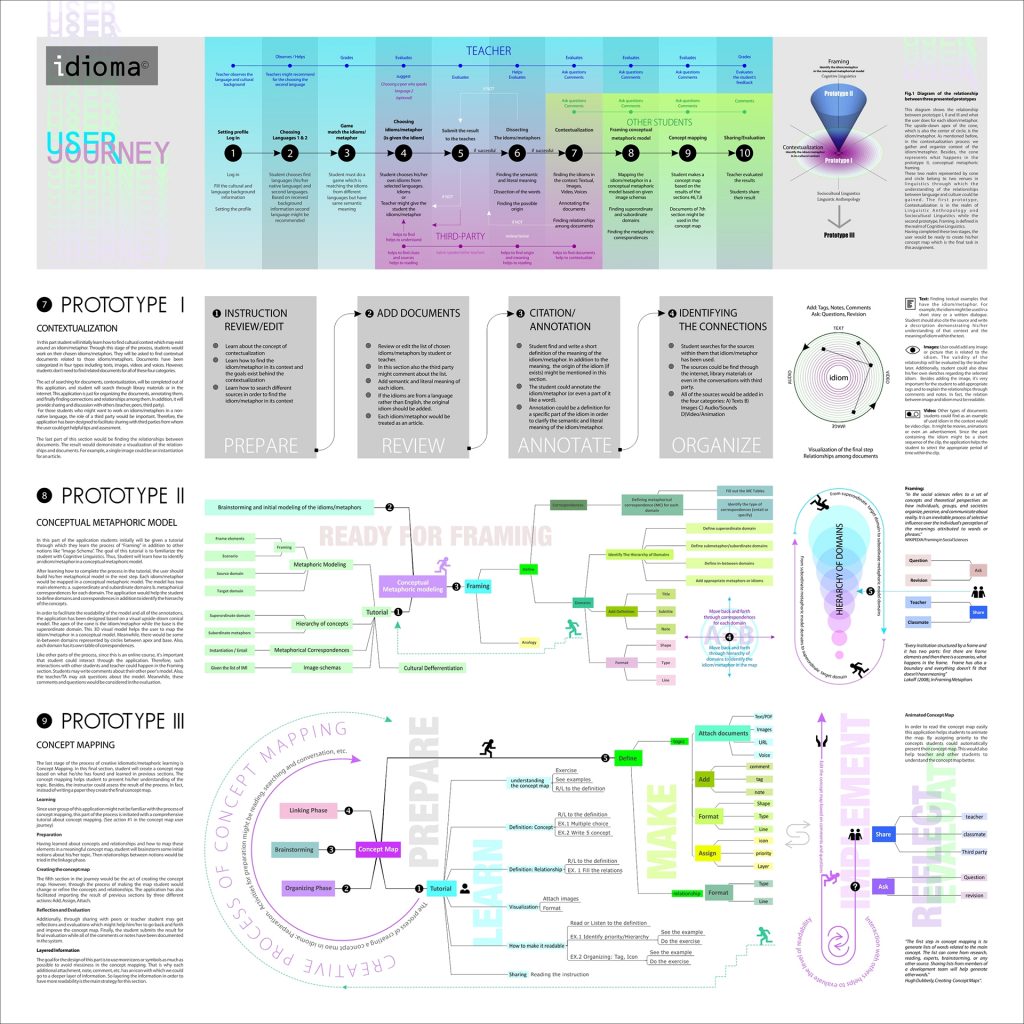
User Journey Map and Task Flow
Prototype 1: Contextualization and Annotating Documents
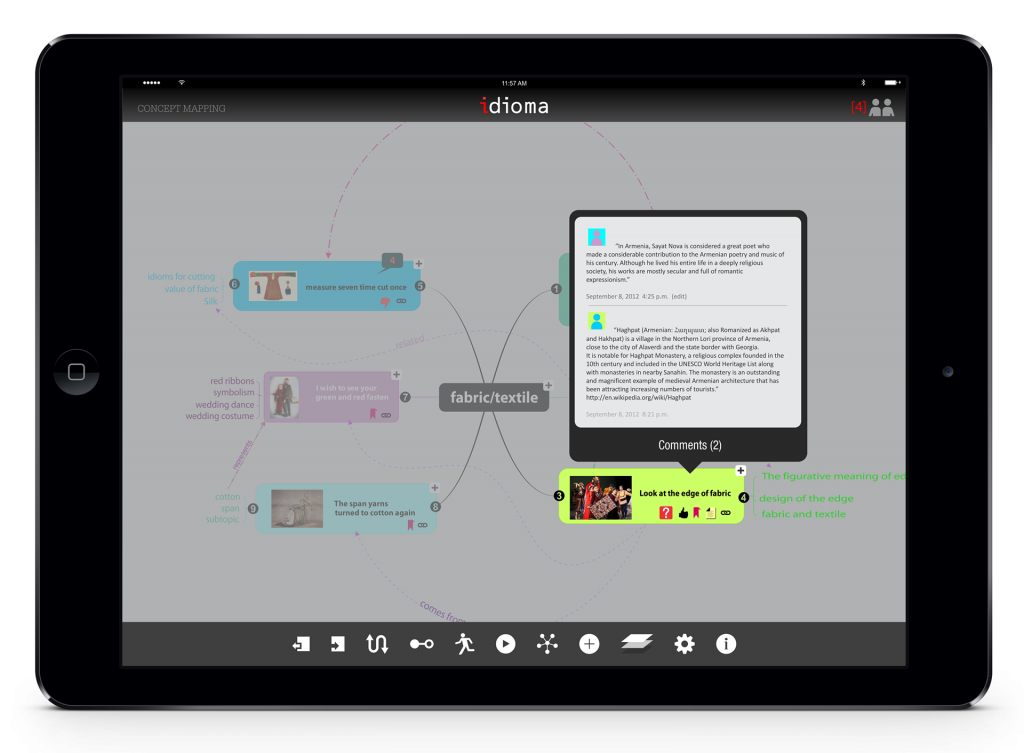
In this part student will initially learn how to find cultural context which may exist around an idiom/metaphor. Through this stage of the process, students would work on their chosen idioms/metaphors. They will be asked to find contextual documents related to those idioms/metaphors. Documents have been categorized in four types including texts, images, videos and voices. However, students don’t need to find related documents for all of these four categories.
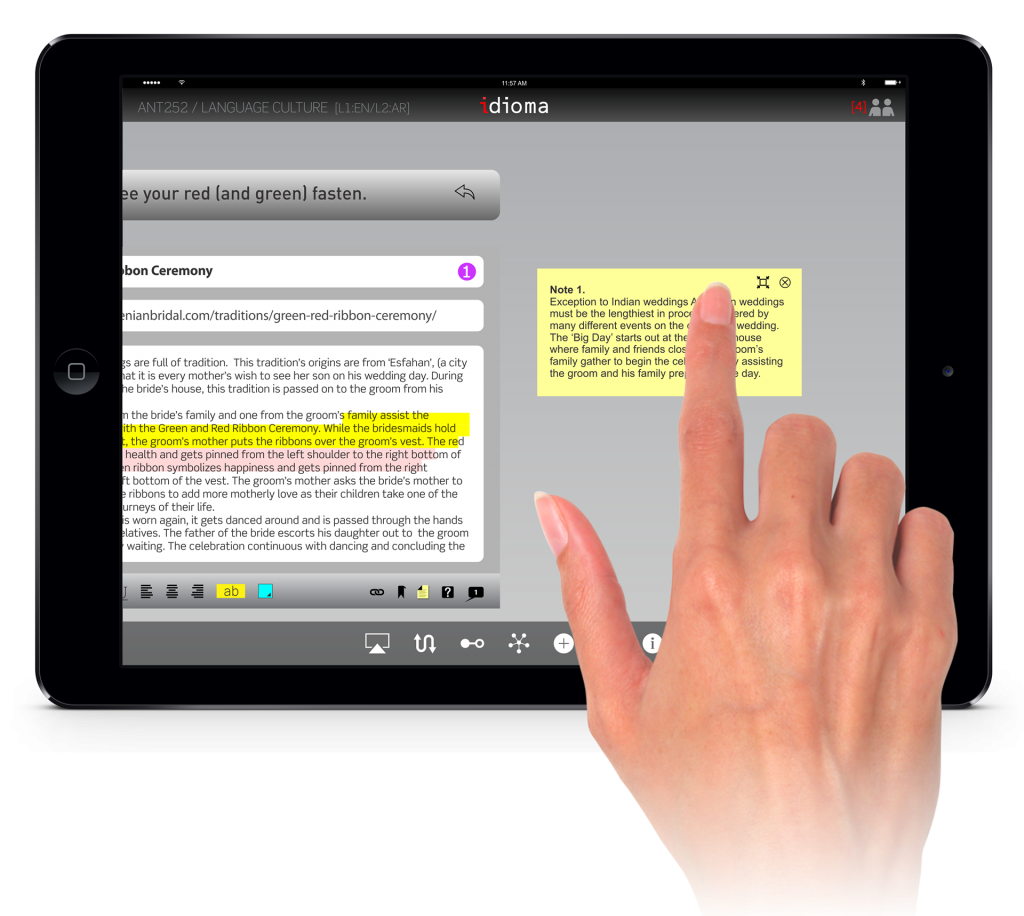
The user can annotate, write notes or mark up the documents that he/she find related to idioms.
The act of searching for documents, contextualization, will be completed out of this application, and student will search through library materials or in the internet. This application is just for organizing the documents, annotating them, and finally finding connections and relationships among them. In addition, it will provide sharing and discussion with others (teacher, peers, third party).
For those students who might want to work on idioms/metaphors in a non-native language, the role of a third party would be important. Therefore, the application has been designed to facilitate sharing with third parties from whom the user could get helpful tips and assessment.

The user can organize all of information and documents he/she find in different categories. The default classification is based on the media type such as textual, images, audio, and videos. However, the user may define other categories if it is necessary.
The last part of this section would be finding the relationships between documents. The result would demonstrate a visualization of the relationships and documents. For example, a single image could be an instantiation for an article.
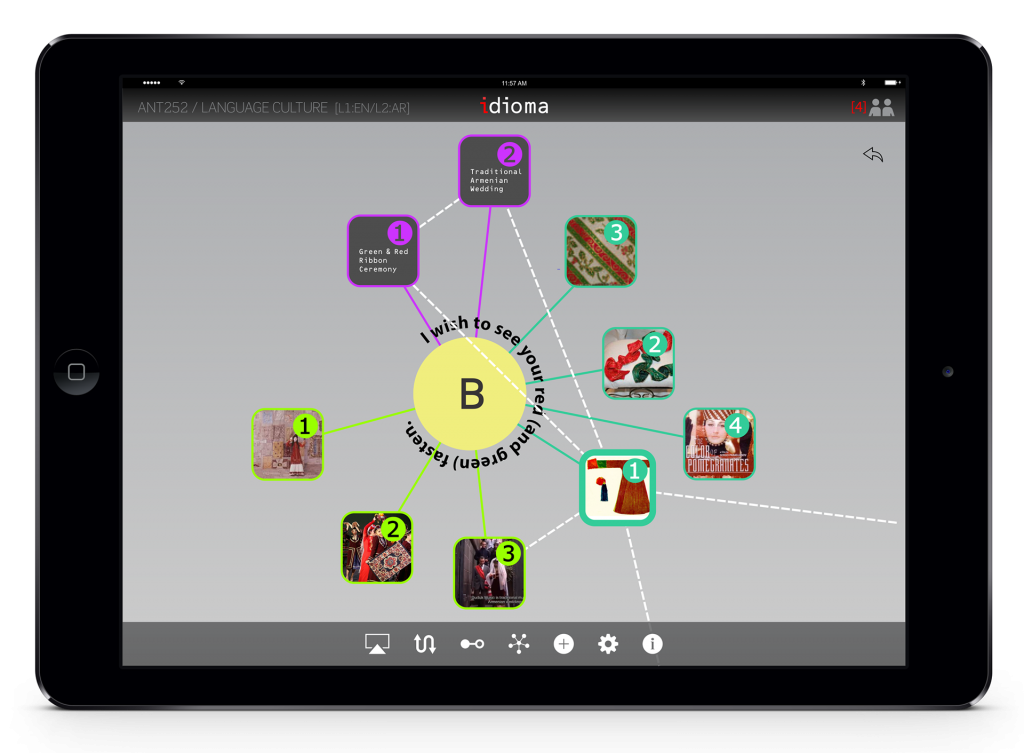
The user can organizes the contents around an idiom.
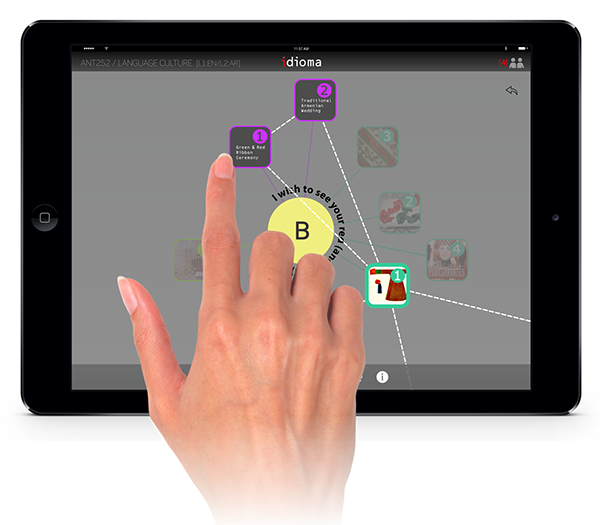
Students will be able to build a relationship between different contents and add their own interpretation, comments, or annotation. These diagram will be used in the next stages in order to create a concept map.
Prototype 2: Building a Conceptual Metaphoric Model
In this part of the application students initially will be given a tutorial through which they learn the process of “Framing” in addition to other notions like “Image-Schema”. The goal of this tutorial is to familiarize the student with Cognitive Linguistics. Thus, Student will learn how to identify an idiom/metaphor in a conceptual metaphoric model.
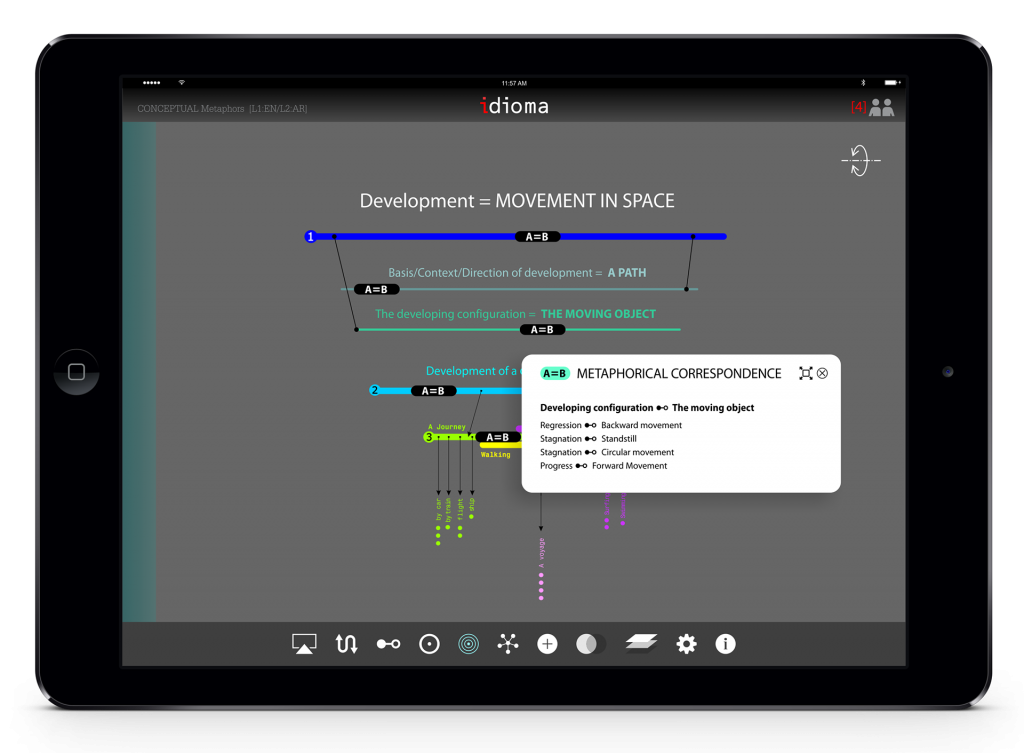
After learning how to complete the process in the tutorial, the user should build his/her metaphorical model in the next step. Each idiom/metaphor would be mapped in a conceptual metaphoric model. The model has two main elements: a. superordinate and subordinate domains b. metaphorical correspondences for each domain. The application would help the student to define domains and correspondences in addition to identify the hierarchy of the concepts.
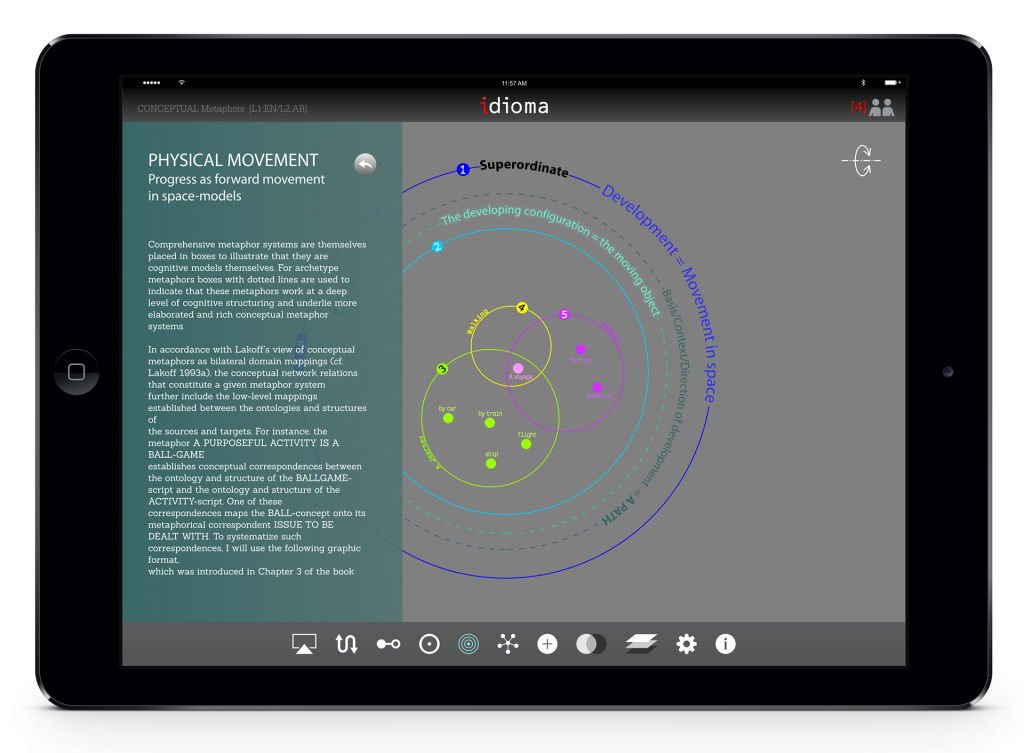
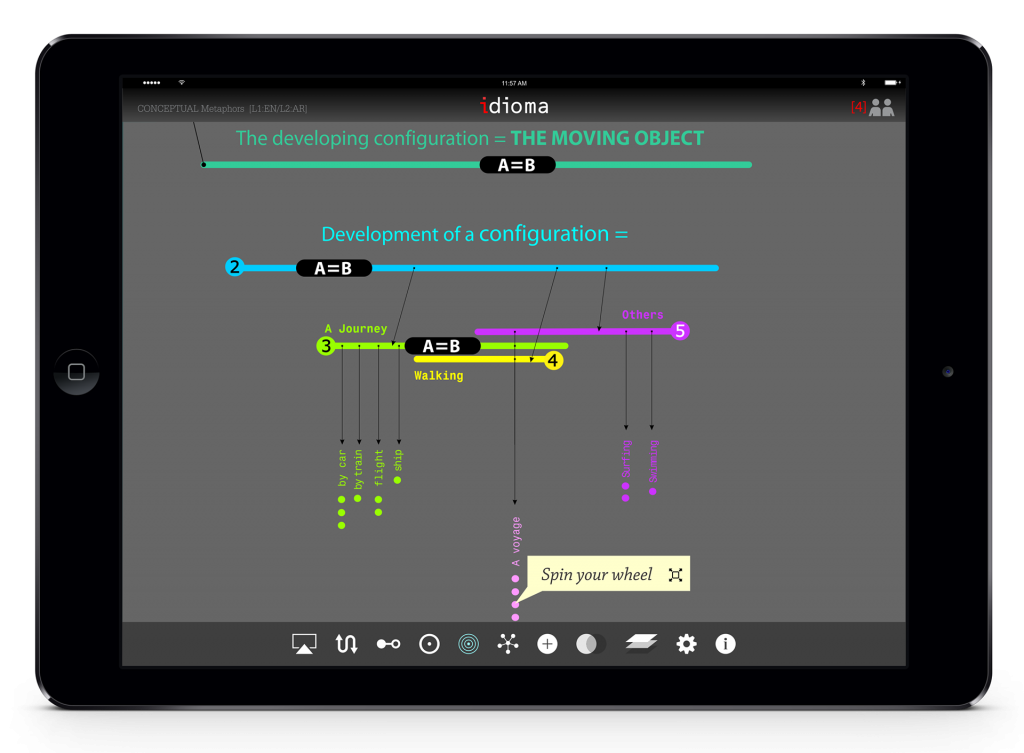
The app facilitates making a three dimensional model for idioms. This hierarchical organization helps student to understand the metaphoric aspects of idioms through making a visual model. Here, the user may see the model from top view. The hierarchical models are conical and there are in two modes: top view and elevation view. The user can simply switch between these two modes.
In order to facilitate the readability of the model and all of the annotations, the application has been designed based on a visual upside-down conical model. The apex of the cone is the idiom/metaphor while the base is the superordinate domain. This 3D visual model helps the user to map the idiom/metaphor in a conceptual model. Meanwhile, there would be some in-between domains represented by circles between apex and base. Also, each domain has its own table of correspondences.
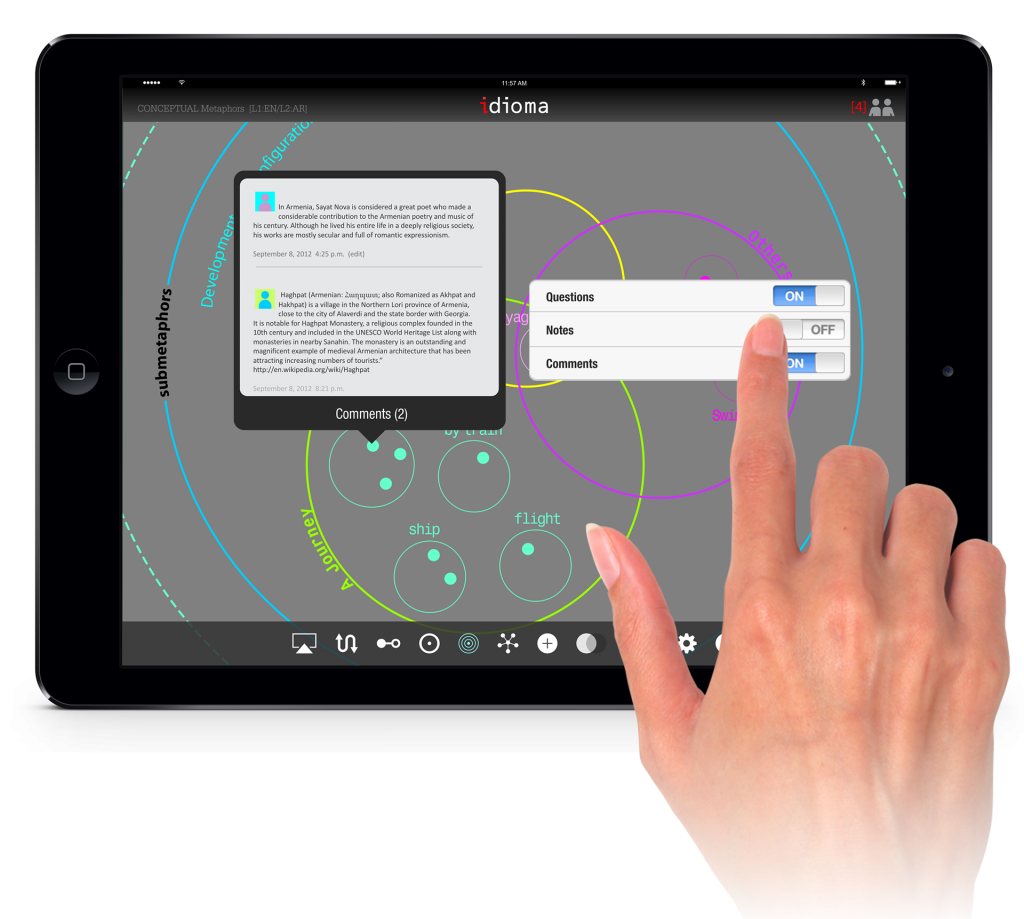
Like other parts of the process, since this is an online course, it’s important that student could interact through the application. Therefore, such interactions with other students and teacher could happen in the Framing section. Students may write comments about their other peer’s model. Also, the teacher/TA may ask questions about the model. Meanwhile, these comments and questions would be considered in the evaluation.
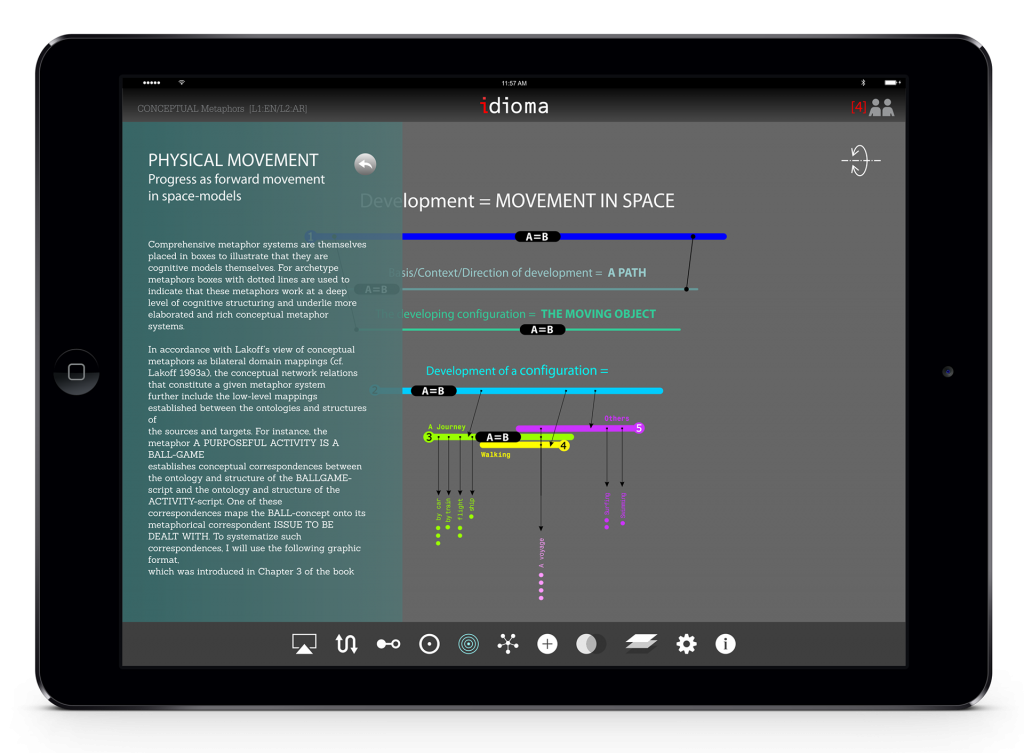
The user can organize and interact differently withe model in the vertical mode.
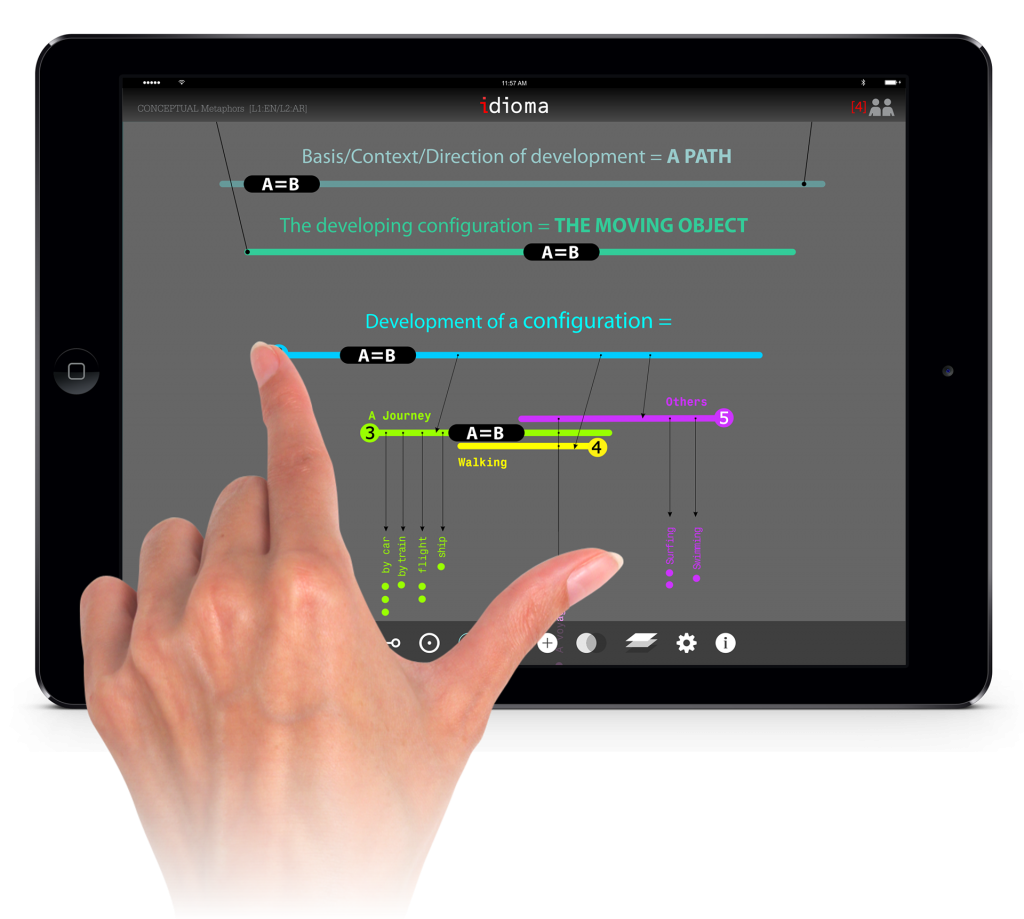
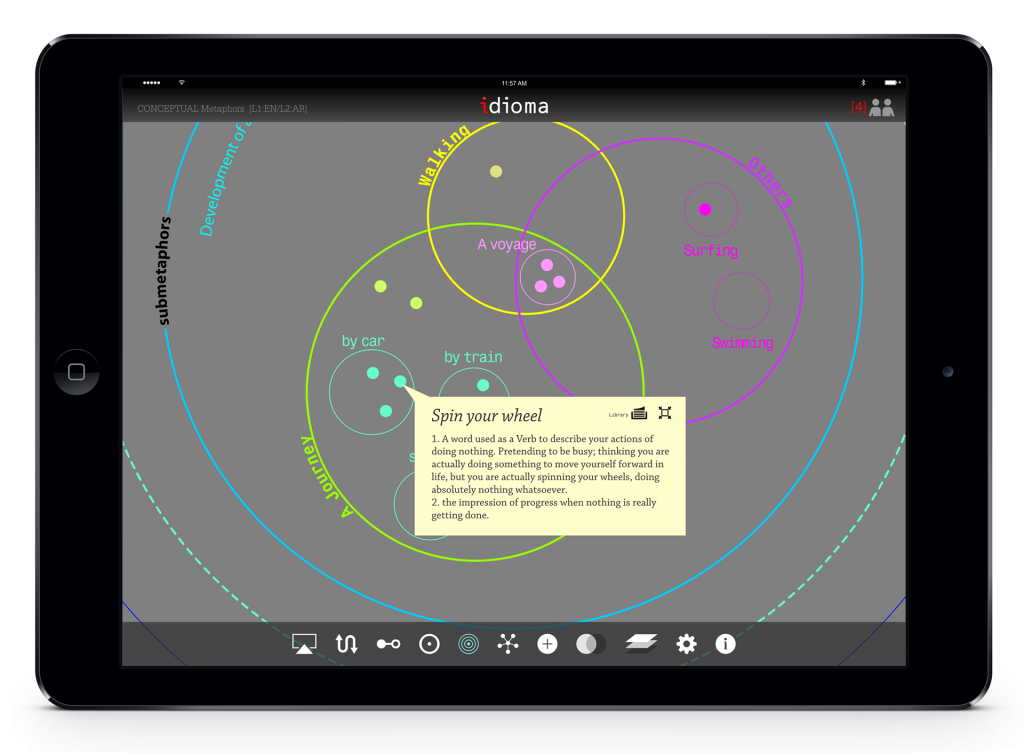
The model has different layer of information, once the user zoom in, more information will be appeared.
Like top view mode, the user may add annotation or comment. Student also can define relationships between concepts.
Prototype 3: Concept Mapping
The last stage of the process of creative idiomatic/metaphoric learning is Concept Mapping. In this final section, student will create a concept map based on what he/she has found and learned in previous sections. The concept mapping helps student to present his/her understanding of the topic. Besides, the instructor could assess the result of the process. In fact, instead of writing a paper they create the final concept map.
Learning
Since user group of this application might not be familiar with the process of concept mapping, this part of the process is initiated with a comprehensive tutorial about concept mapping. (See action #1 in the concept map user journey)
Preparation
Having learned about concepts and relationships and how to map these elements in a meaningful concept map, student will brainstorm some initial notions about his/her topic. Then relationships between notions would be tried in the linkage phase.
Creating the concept map
The fifth section in the journey would be the act of creating the concept map. However, through the process of making the map student would change or refine the concepts and relationships. The application has also facilitated importing the result of previous sections by three different actions: Add, Assign, Attach.
Reflection and Evaluation
Additionally, through sharing with peers or teacher student may get reflections and evaluations which might help him/her to go back and forth and improve the concept map. Finally, the student submits the result for final evaluation while all of the comments or notes have been documented in the system.
Layered Information
The goal for the design of this part is to use more icons or symbols as much as possible to avoid messiness in the concept mapping. That is why each additional attachment, note, comment, etc. has an icon with which we could go to a deeper layer of information. So layering the information in order to have more readability is the main strategy for this section.
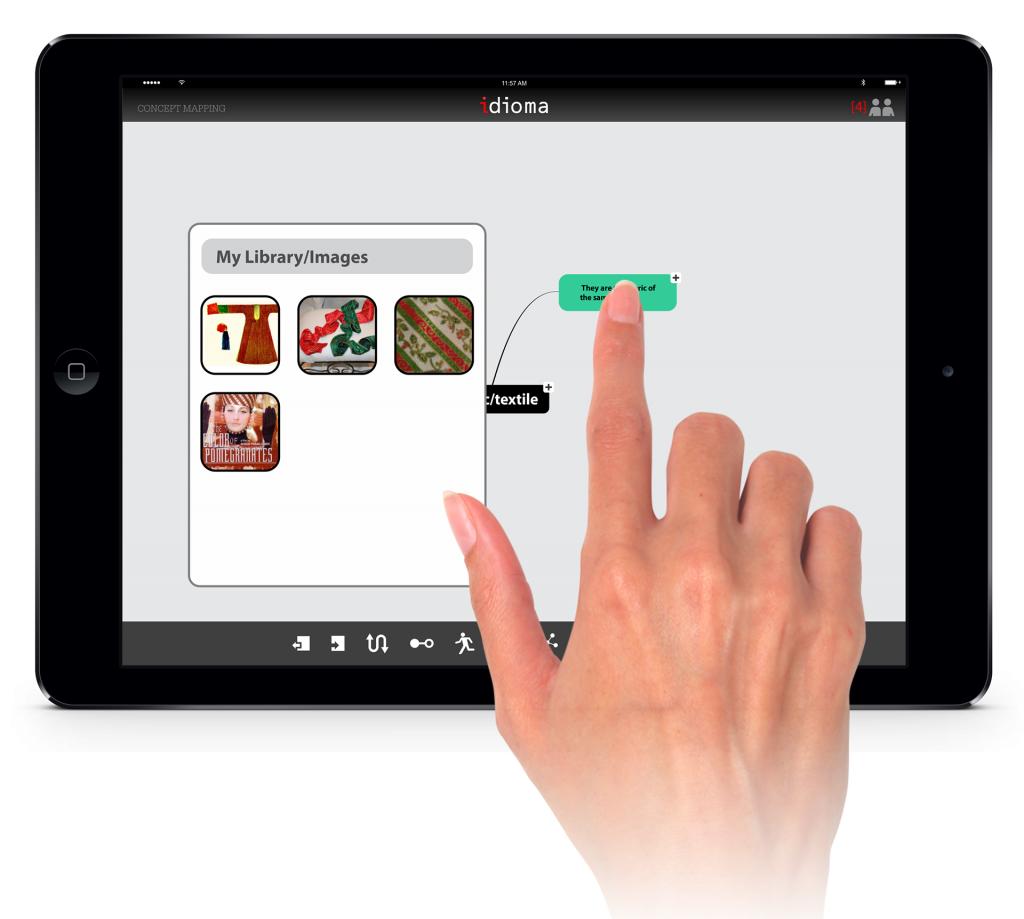
The last step in this app is making a concept map, which would be their final output for the course. Students will use the contents and models that they have created in the previous stages of the process to make the interactive and multimedia-based concept map.
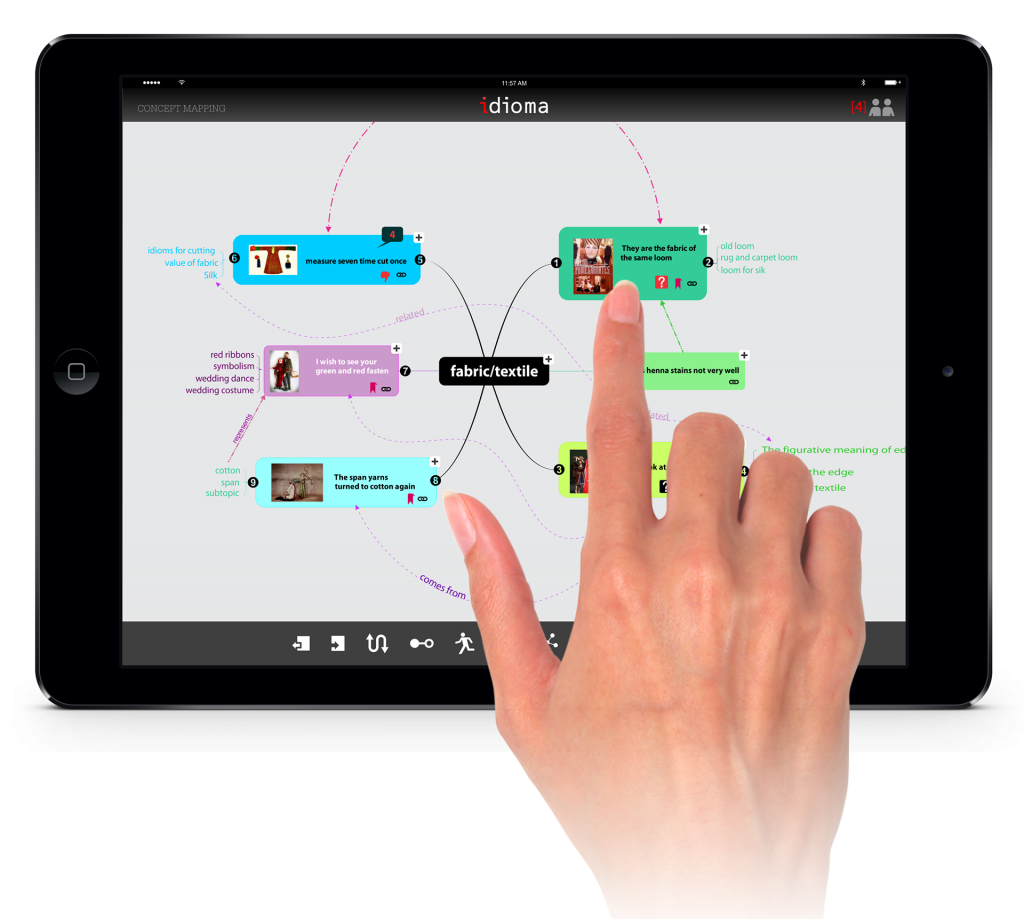
The user may embed all kind of digital materials to the map. Students will also be able to connect the concepts and define the relationships. The final concept maps must be animated so that everyone can understand the process.
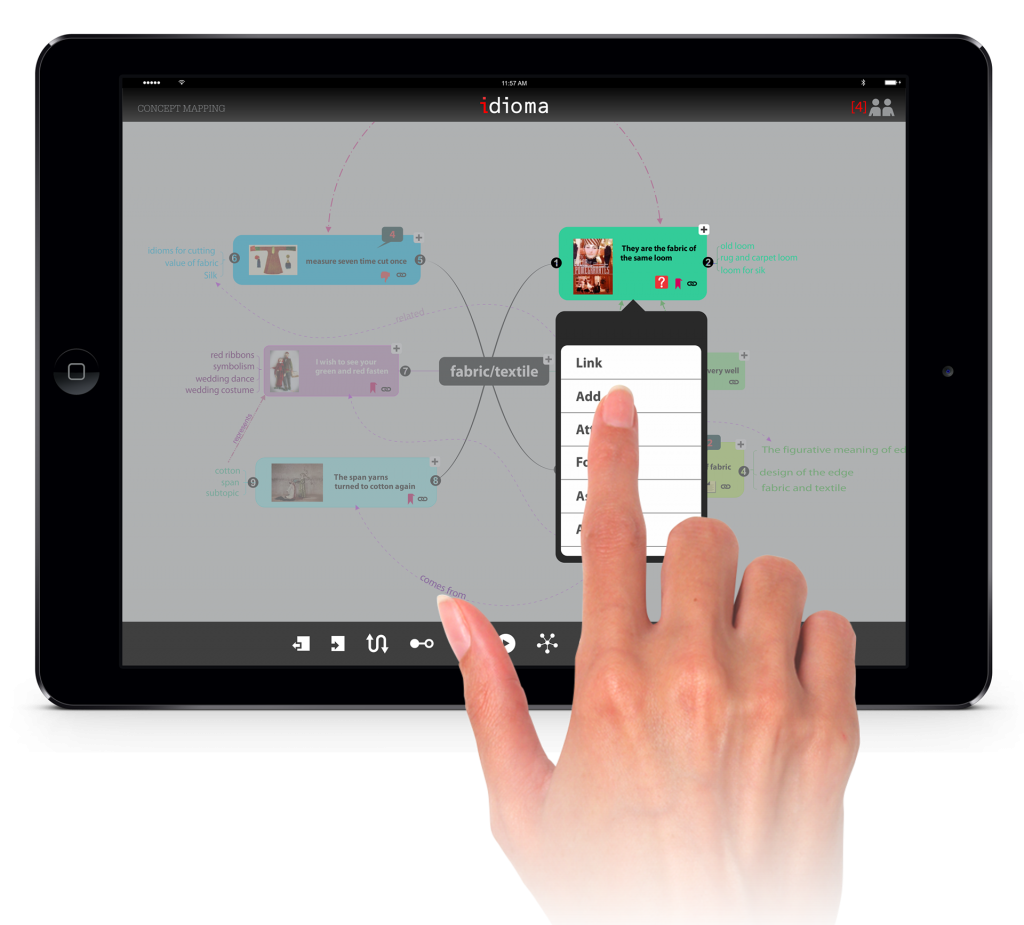
Concept maps in this system are shared. Students and instructor may add comments or notes for every map.